A woman's fertility decreases with age, due to decreased number of eggs left in the ovaries.
According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), fertility gradually and consistently decreases from age 30, and more drastically after age 35: "Every month she tries, a healthy, fertile 30-year-old woman has a 20% chance of getting pregnant. That means that for every 100 fertile 30-year-old women trying to get pregnant in a cycle, 20 will succeed and the remaining 80 will have to try again. At the age of 40, a woman's probability is less than 5% per cycle; therefore, fewer than 5 out of 100 women are expected to succ
eed each month." Unlike the early decline in female fertility, the decrease in the fertile characteristics of man's sperm occurs much later and does not pose a problem until after
age 60. That's why® we recommend that women who want to postpone motherhood consider egg cryopreservation as their family's planning option.
Egg freezing
Complexity: Medium (requires surgery and sedation).
Indications:
- Preservation of fertility for personal and/or social reasons, also called "Maternity banking".
- Egg donation.
- Women with different types of cancer that require chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy that may be harmful to future ovarian function.
- Surgeries that can cause damage to the ovaries.
- Risk of premature ovarian failure due to chromosomal abnormalities or a family history of early menopause (before age 35).
- Ovarian diseases at risk of damage to the ovaries (e.g. advanced endometriosis).
- Genetic mutations that require removal of the ovaries.
- For trans people.
How is egg freezing performed?
- First, the fertility specialist performs an evaluation of the ovarian reserve (quantity and quality of eggs in the ovaries) that includes blood tests for hormonal measurements and a transvaginal ultrasound at specific times in the menstrual cycle.
- Ovarian stimulation is then performed using injectable and/or oral hormone medications prescribed on the basis of testing.
- When the follicles reach a size of 18-20 mm, the eggs are aspirationd transvaginally.The maturity of the eggs is evaluated under the microscope, and those that are mature are cryopreservan at -196oC in liquid nitrogen to maximize their preservation. Currently, vitrification is the method of choice for cryoconserving eggs.
How will eggs be used in the future?
- When the woman decides to carry out a pregnancy, her cryopreservated eggs are thawed.
- Eggs that survive the thawing process are fertilized by an intracytoplemic sperm injection where a single sperm is injected directly into the egg.
- The embryos are grown 5 days before being transferred into the woman's uterus. The remaining embryos are vitrified again for later use. It is important
to note that in case of pregnancy, the rates of genetic or chromosomal abnormalities of the gestational product are those corresponding to the age at which the eggs were cryopreservated and not at the age at which they devitrificate and produce the pregnancy.
Egg freezing success rates:
Clinical pregnancy rates have been estimated to be between 5-12% per egg, or 25% per embryo transfer cycl
e. The two most influential factors are maternal age at the time of egg freezing and the number of eggs available.
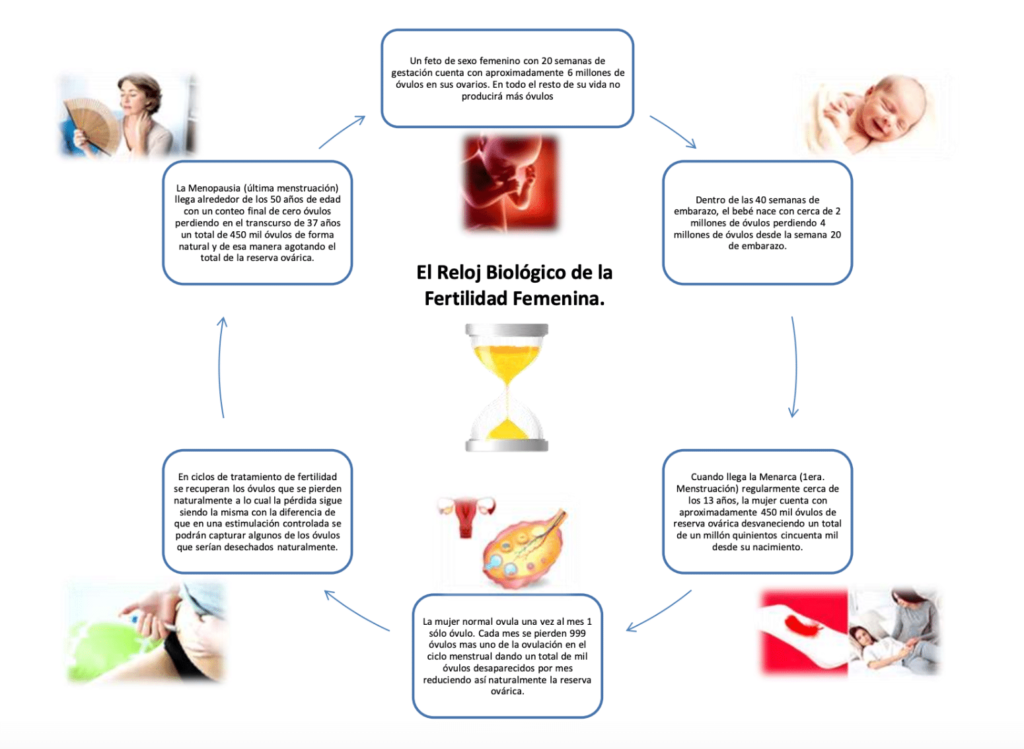
What is the "biological clock"?
Sperm cryopreservation
Semen freezing is a method used to preserve male fertility and allow for future pregnancy.
Indications:
- Semen donation.
- Preservation of fertility for social or personal reasons to delay paternity.
- Prior to a vasectomy.
- Severe male factor. (Try to accumulate several semen samples to increase the amount of sperm).
- Testicular and/or epididimaria biopsies in patients with no sperm in ejaculation (azoospermia) or with very decreased amounts and/or quality of sperm in semen. (MESA and TESA).
- Men with cancer who require chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy that may negatively affect future testicular function.
- Premortem and postmortem cryopreservation
- High-risk occupations to testicular damage.
- For trans people.
Complexity:
- By masturbation: come down.
- By testicular biopsy or epididimaria: median.
How is sperm freezing performed?
Cryopreservated sperm are frozen in liquid nitrogen at a temperature of -196oC. Frozen sperm cells remain in a suspended animation state and all cellular activity essentially stops until thawing. After thawing, a percentage of sperm revives and returns to the pre-freezing state.
Semen Freezing Success Rates:
It is estimated that 50% of frozen sperm survive thawing while preserving their pre-freezing motility and morphology characteristics.Fertility of this type of sperm depends on the quality and quantity found in pre-ejaculated semen.
Success rates in producing embryos and pregnancies in In Vitro Fertilization or Intracytoplemic Sperm Injection.